terminal cheatsheet
dir structure
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
| bin | Essential command binaries. No subdirectories in /bin. |
| boot | Static files of the boot loader |
| dev | Device files |
| etc | Host-specific system configuration |
| lib | Essential shared libraries and kernel modules |
| media | Mount point for removeable media |
| mnt | Mount point for mounting a filesystem temporarily |
| opt | Add-on application software packages |
| sbin | Essential system binaries |
| srv | Data for services provided by this system |
| tmp | Temporary files |
| usr | Secondary hierarchy |
| var | Variable data |
Each directory listed above is specified in detail in separate subsections below.
/usr and /var each have a complete section in this document due to the complexity of those directories.
The following commands, or symbolic links to commands, are required in /bin.
Command Description cat Utility to concatenate files to standard output chgrp Utility to change file group ownership chmod Utility to change file access permissions chown Utility to change file owner and group cp Utility to copy files and directories date Utility to print or set the system data and time dd Utility to convert and copy a file df Utility to report filesystem disk space usage dmesg Utility to print or control the kernel message buffer echo Utility to display a line of text false Utility to do nothing, unsuccessfully hostname Utility to show or set the system's host name kill Utility to send signals to processes ln Utility to make links between files login Utility to begin a session on the system ls Utility to list directory contents mkdir Utility to make directories mknod Utility to make block or character special files more Utility to page through text mount Utility to mount a filesystem mv Utility to move/rename files ps Utility to report process status pwd Utility to print name of current working directory rm Utility to remove files or directories rmdir Utility to remove empty directories sed The `sed' stream editor sh The Bourne command shell stty Utility to change and print terminal line settings su Utility to change user ID sync Utility to flush filesystem buffers true Utility to do nothing, successfully umount Utility to unmount file systems uname Utility to print system information If /bin/sh is not a true Bourne shell, it must be a hard or symbolic link to the real shell command.
The [ and test commands must be placed together in either /bin or /usr/bin.
Tip Rationale
For example bash behaves differently when called as sh or bash. The use of a symbolic link also allows users to easily see that /bin/sh is not a true Bourne shell.
Specific Options The following programs, or symbolic links to programs, must be in /bin if the corresponding subsystem is installed:
Command Description csh The C shell (optional) ed The `ed' editor (optional) tar The tar archiving utility (optional) cpio The cpio archiving utility (optional) gzip The GNU compression utility (optional) gunzip The GNU uncompression utility (optional) zcat The GNU uncompression utility (optional) netstat The network statistics utility (optional) ping The ICMP network test utility (optional) If the gunzip and zcat programs exist, they must be symbolic or hard links to gzip. /bin/csh may be a symbolic link to /bin/tcsh or /usr/bin/tcsh.
Tip Rationale
The tar, gzip and cpio commands have been added to make restoration of a system possible (provided that / is intact).
Conversely, if no restoration from the root partition is ever expected, then these binaries might be omitted (e.g., a ROM chip root, mounting /usr through NFS). If restoration of a system is planned through the network, then ftp or tftp (along with everything necessary to get an ftp connection) must be available on the root partition.
Specific Options The following directories, or symbolic links to directories must be in /etc, if the corresponding subsystem is installed:
Directory Description opt Configuration for /opt The following files, or symbolic links to files, must be in /etc if the corresponding subsystem is installed: [6]
File Description csh.login Systemwide initialization file for C shell logins (optional) exports NFS filesystem access control list (optional) fstab Static information about filesystems (optional) ftpusers FTP daemon user access control list (optional) gateways File which lists gateways for routed (optional) gettydefs Speed and terminal settings used by getty (optional) group User group file (optional) host.conf Resolver configuration file (optional) hosts Static information about host names (optional) hosts.allow Host access file for TCP wrappers (optional) hosts.deny Host access file for TCP wrappers (optional) hosts.equiv List of trusted hosts for rlogin, rsh, rcp (optional) hosts.lpd List of trusted hosts for lpd (optional) inetd.conf Configuration file for inetd (optional) inittab Configuration file for init (optional) issue Pre-login message and identification file (optional) ld.so.conf List of extra directories to search for shared libraries (optional) motd Post-login message of the day file (optional) mtab Dynamic information about filesystems (optional) mtools.conf Configuration file for mtools (optional) networks Static information about network names (optional) passwd The password file (optional) printcap The lpd printer capability database (optional) profile Systemwide initialization file for sh shell logins (optional) protocols IP protocol listing (optional) resolv.conf Resolver configuration file (optional) rpc RPC protocol listing (optional) securetty TTY access control for root login (optional) services Port names for network services (optional) shells Pathnames of valid login shells (optional) syslog.conf Configuration file for syslogd (optional) mtab does not fit the static nature of /etc: it is excepted for historical reasons. [7]
change hostname
homedir
getting manual
domain
apps
sudo ## if sudo doesnt exist
ipcalc ## calculate ip net
tree ## print dir structure
btop ## monitor
whois ## who is ?
perf ## speedtest generator
deja-dup ## simple backup
parted ## disk util
gparted ## disk util
screenfetch ## show info
screenfetch -n
tweaks ## system util gui
nautilus ## file manager gui
lastlog ## show last user
tldr ## show most useful commands for every package
curl
curl cheat.sh/<package> ## like tldr
insight
the -a option should be passed to see all files. by default tree does not print hidden files (those beginning with a dot ‘.’). In no event does tree print the file system constructs ‘.’ (current directory) and ‘..’ (previous directory).
to list directories only
random stuff
to get su
show user
screen
run command in background while closing ssh session
show open screen sessions
start a new named screen session
detach from inside a screen
reattach to an open screen
start a new daemon and log the output to screenlog.x
kill the current screen session: Ctrl + A, K or exit
history
Note
all inputs are logged in ~/.bash_history
delete history
change default history size 500 in ~/.bashrc
or run HISTSIZE=copy & paste in terminal
Note
sometimes just highlighting does copy the text or copy it with pressing scrollwheel
delete
delete folder and its files
umask
umask stands for user mask
| Mask | Files | Directories |
|---|---|---|
| 000 | 666 (rw-rw-rw-) | 777 (rwxrwxrwx) |
| 002 | 664 (rw-rw-r--) | 775 (rwxrwxr-x) |
| 007 | 660 (rw-rw----) | 770 (rwxrwx---) |
| 022 | 644 (rw-r--r--) | 755 (rwxr-xr-x) |
| 027 | 640 (rw-r-----) | 750 (rwxr-x---) |
| 077 | 600 (rw-------) | 700 (rwx------) |
| 277 | 400 (r--------) | 500 (r-x------) |
The digits you can use and what they represent are listed here:
0: (000) No permission. 1: (001) Execute permission. 2: (010) Write permission. 3: (011) Write and execute permissions. 4: (100) Read permission. 5: (101) Read and execute permissions. 6: (110) Read and write permissions. 7: (111) Read, write, and execute permissions.
permission
who own files
who has permission
sourceuser and groups
sudo passwd root sudo passwd sudo su
user
getent passwd cat /etc/passwd
useradd -D useradd ## Manual guided adduser ## Automatic
group
getent group
less /etc/group
groups
show open ports
or
dmesg
kernel
show logs when its not directly kernel relevated show last boot messagesfollow logs
fstab
ls -al /dev/disk/by-uuid lsblk -lf nano /etc/fstab UUID=XXXXXXXXXXXXX ext4 auto 0 0
fqdn
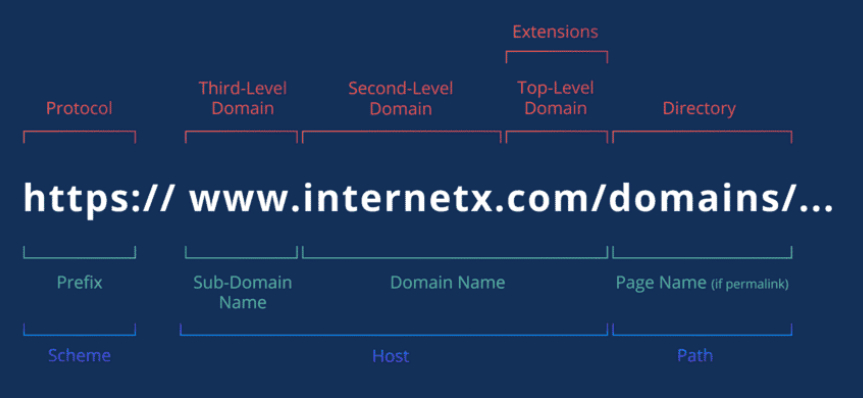
dns stuff
reverse lookup
logs
disk
link: unix filesystem
list disk
by id or uuid
ls -al /dev/disk/by-uuid/ ls -al /dev/disk/by-id/
by sdX
lsblk shows the size of the partition. df shows the size of the filesystem that's on that partition. A partition can contain a smaller filesystem. One common cause for that is writing a filesystem image to a larger partition.
list all mounted disk
for mounted and unmounted
adjust filesystem to partition. it takes some time to do this after enter following command
NO DAILY USE
format disk
new hdd
if alreaady formatted and mounted
umount /dev/<disk>
lsof <mountpoint> # if umount doesnt work bc target is busy then ...
kill PID # normally its bc of finder
mkfs.<filesystem> /dev/<disk>
mkdir /mnt/<dir>
mount /dev/<disk> /mnt/<dir>
repair disk
when disk cant be mounted or disk is corrputed
calculate disk space
will sort the folders by size. Helpful when looking to clear space..
used when human-readable mode
copy
copy files from local drive to external drive
copy on block level
rename
system
install & delete app
preparation
apt
search
apt-cache search <package>
apt-cache search <package> | less
apt-cache search .
apt search <package>
install
apt install <package>
apt --install-recommends install
--no-install-recommends
apt --install-suggest install
--no-install-suggests
dpkg -i <>.deb
reinstall
remove
dpkg
does not install any depencies
does install depencies
Install
Remove Purgeappimage
download file
rename dir
if destination dir doesn't exist, source dir will get renamed
os version
firmware
debian 12 has fwupd-service for updating firmware of connected devices. awesome!
peripherals
ui/ux
change mousecursor
Note
debian
Folder with cursor.theme und index.theme in it has to be in /usr/share/icons
Afterwards in Tweaks (apt install gnome-tweaks) under Appearance > Cursor choose your cursor
gui installation
turn ethernet online
lspci | grep -i ethernet
ip link show enp1s0
sudo ip link set enp1s0 up
sudo systemctl restart networking
sudo nano /etc/apt/sources.list
deb http://deb.debian.org/debian bookworm main contrib non-free non-free-firmware
sudo apt install firmware-linux-nonfree
sudo apt install nivida-driver
some default apps
figlet
tree
btop
htop
sudo (if debianinstaller got rootpw, debian doesnt install sudo)
docker engine
stress
ipcalc
Text
Settings > Accessibility > Large Text
save output into txt
cat file2 >> file1
cat *.txt >> newfile.txt
|| visible in terminal || visible in file || existing
Syntax || StdOut | StdErr || StdOut | StdErr || file
==========++==========+==========++==========+==========++===========
> || no | yes || yes | no || overwrite
>> || no | yes || yes | no || append
|| | || | ||
2> || yes | no || no | yes || overwrite
2>> || yes | no || no | yes || append
|| | || | ||
&> || no | no || yes | yes || overwrite
&>> || no | no || yes | yes || append
|| | || | ||
| tee || yes | yes || yes | no || overwrite
| tee -a || yes | yes || yes | no || append
|| | || | ||
n.e. () || yes | yes || no | yes || overwrite
n.e. () || yes | yes || no | yes || append
|| | || | ||
|& tee || yes | yes || yes | yes || overwrite
|& tee -a || yes | yes || yes | yes || append
compress
https://www.cyberciti.biz/faq/how-to-create-tar-gz-file-in-linux-using-command-line/
tar
tar command option Description -c Create a new archive -x Extract files from an archive -t List the contents of an archive -v Verbose output -f file.tar.gz Use archive file -C DIR Change to DIR before performing any operations -z Filter the archive through gzip i.e. compress or decompress archive
tar -czvf filename.tar.gz /path/to/dir1 tar -czvf filename.tar.gz /path/to/dir1 dir2 file1 file2
Create a tar.gz file from all pdf (".pdf") files
tar -czvf archive.tgz *.pdf
- tar -cf archiv.tar datei/ordner: Archiv erstellen
- tar -xf archiv.tar: Archiv entpacken
- tar -tvf archiv.tar: Inhalt eines Archivs anzeigen
- tar -czf archiv.tar.gz datei/ordner: Archiv erstellen und komprimieren (gzip)
- tar -xzf archiv.tar.gz: Gzip-komprimiertes Archiv entpacken
- tar -rf archiv.tar datei: Datei zu bestehendem Archiv hinzufügen
- tar -uf archiv.tar datei: Archiv aktualisieren
- tar --delete -f archiv.tar datei: Datei aus Archiv löschen
gzip
- gzip datei: Datei komprimieren
- gzip -d datei.gz: Gzip-Datei entpacken
- gzip -k datei: Komprimieren, Originaldatei behalten
- gzip -r ordner: Alle Dateien im Ordner rekursiv komprimieren
- gzip -t datei.gz: Komprimierte Datei auf Integrität prüfen
- gzip -l datei.gz: Informationen über die komprimierte Datei anzeigen